Hotspot support allows words on the terminal screen to act as AID generating keys, active URL links, active e-mail links, active UNC links, active file links or a launch pad for a script. This powerful support allows users to click on words on the terminal screen to cause an action. For example:
| • | You user could click on the word "F1" to rather than pressing the F1 key. |
| • | You could click on "http://companyname.com" to activate the web browser and open the company web site. |
| • | You could click on "support@sdisw.com" to start your e-mail client and pass it the e-mail address. |
| • | You could click on file://c:/test.txt to open a file. |
| • | You could click on \\servername\sharename\file.ext to open a shared file. |
| • | If there is a script that corresponds to a word on the screen, then the script is run when the word is clicked. For example, clicking on "Help" would cause the "help.txt" script to run. |
To activate Hotspot support, you need to assign the Hotspot terminal function to a mouse button as follows:
| 1. | Open the Setup menu and select Keyboard... |
| 2. | In the Keyboard pane of the Session Setup dialog box, click the Configure... button. |
| 3. | In the Keyboard Setup dialog box, select "Terminal Keys" in the Function Group drop-down list box. |
| 4. | Select Hotspot in the Function list box. |
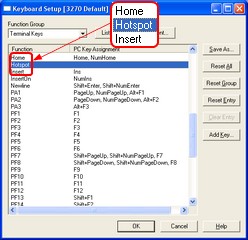
| 5. | Click the Add Key... button. |
| 6. | Click the desired mouse button over the text in the Type Key dialog box. |
| 7. | Click the OK button in the Type Key dialog box. |
| 8. | Click the OK button in the Keyboard Setup dialog box. |
| 9. | Click the OK or Apply button in the Session Setup dialog box. |
Once the mouse button is assigned, clicking that button causes the word under the mouse pointer to be examined and appropriate actions is taken. The following type of hotspots are supported.
Hotspot type |
Action |
AID key |
If the hotspot is an AID generating key, then the corresponding AID key is sent to the host. |
Web site |
If the hotspot begins with 'http://', 'https://' or "www." then the default web browser is launched and passed that URL. |
E-mail address. |
If the hotspot starts with "maiIto:" or looks like an e-mail address then the default e-mail client is launched and passed the e-mail address. |
UNC link |
If the hotspot starts with \\servername\ then the file name is sent to the windows shell to be opened. |
File link |
If the hotspot starts with file:/// then the file name is sent to the windows shell to be opened. |
Script |
If the word is not one of the above, then a check is made to see if a script with that word name exists (wordname.txt). If found, the script is executed. |
If a Hotspot is not recognized then the cursor is moved to the mouse pointer location and the ENTER key is sent to the host (simulating a menu selection).
An AID key identifier is delimited by a space, null, or attribute byte at the beginning and a space, null, attribute byte or non alpha-numeric character at the end. An e-mail address, URL, UNC or file link or or word is delimited by a space, null or attribute byte at the beginning and the end.
AID Generating Keys:
3270: PF1 - PF24, PA1 - PA3, CLEAR or ENTER
5250: F1 - F24, PA1 -PA3, CLEAR, ENTER or HELP
TN3270 Plus is continually being improved. To learn more about the latest enhancements, please review our Version History web page.


